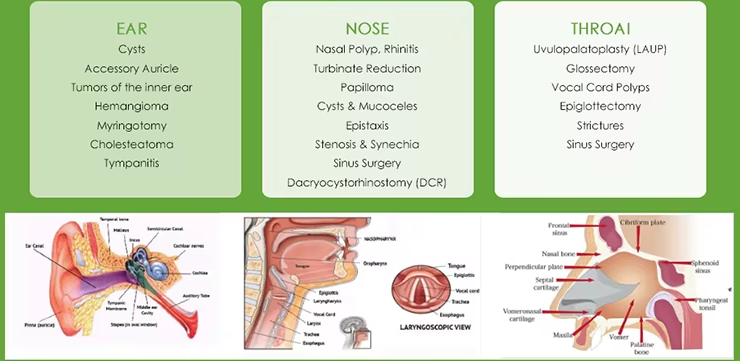
ENT

980nm and 1470nm diode lasers are widely used in ear-nose-throat, due to their tissue-specific absorption and minimally invasive properties.
1. 980nm Diode Laser in ENT
-Advantage: High affinity for hemoglobin, enabling precise hemostasis and targeted treatment of vascular-rich tissues, with minimal damage to surrounding non-vascular structures.
- Key Application:
1. Nasal Cavity Treatments:
- Ablation of nasal hemangiomas and telangiectasias (e.g., hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia), stopping recurrent nasal bleeding via vascular coagulation.
- Reduction of inferior turbinate hypertrophy: Shrink vascularized turbinate tissue to improve nasal ventilation, avoiding excessive damage to mucosal function.
2. Throat & Laryngeal Treatments:
- Removal of small vocal cord polyps/nodules (especially vascular ones): Precisely cut lesions with real-time hemostasis, protecting vocal cord mucosal integrity.
- Treatment of chronic pharyngitis: Ablate hyperplastic lymphoid follicles on the posterior pharyngeal wall to relieve sore throat and foreign body sensation.
3. Ear Treatments:
- Management of external auditory canal (EAC) hemangiomas or vascular granulation tissue: Coagulate abnormal blood vessels to remove lesions without damaging EAC skin.
2. 1470nm Diode Laser in ENT
- Advantage: High absorption by water molecules (the main component of soft tissues), generating concentrated thermal effects for efficient tissue cutting, vaporization, and ablation—ideal for treating non-vascular or dense soft tissues.
- Key Application:
1. Nasal Cavity & Sinus Treatments:
- Endoscopic sinus surgery adjuvant: Remove hyperplastic sinus mucosa, polyps, or adhesions, with clear surgical fields and reduced postoperative edema.
- Treatment of nasal septum deviation (during correction): Reshape deviated cartilage/bone tissue with precise cutting, minimizing trauma to nasal septal mucosa.
2. Throat & Laryngeal Treatments:
- Resection of larger laryngeal papillomas or benign tumors: Vaporize tumor tissue layer by layer, reducing the risk of residual lesions and protecting laryngeal function.
- Relief of laryngeal stenosis: Ablate scar tissue in the laryngeal cavity to restore airway patency, with less postoperative scarring.
3. Ear Treatments:
- Removal of EAC cholesteatoma or keratin plugs: Vaporize abnormal keratinous tissue without damaging the underlying EAC bone, lowering the risk of infection recurrence.
Previous:No More
Next:No More
